發佈日期 2025-07-09
如何選擇 COD (化學需氧量)水質分析儀器?

| COD 是什麼? |
|
What is Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)?
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen that must be present in water to oxidize chemical organic materials, like petroleum. COD is used to gauge the short-term impact wastewater effluents will have on the oxygen levels of receiving waters.
化學需氧量(Chemical Oxygen Demand,簡稱COD)是指水體中易被強氧化劑(一般採用重鉻酸鉀)氧化的還原性物質所消耗的氧化劑的量,結果折成氧的量(以mg /L計)。
它是表徵水體中還原性物質的綜合指標。除特殊水樣外,還原性物質主要是有機化合物,組成有機化合物的碳,氮,硫,磷等元素往往處於較低價的氧化價態。
為區別於採用高錳酸鉀作氧化劑的測定,又將此結果稱之為“化學需氧量”或“鉻法COD”,作 “CODcr”,用高錳酸鉀做氧化劑測出的結果稱之為“高錳酸鹽指數”或“錳法COD”,記作“CODMn 高錳酸鹽指數”
COD versus BOD
Like COD, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) measurement can be used to estimate the amount of pollution in a water sample. COD describes the amount of oxygen required to chemically break down pollutants, while BOD indicates the amount of oxygen required to break down organic pollutants biologically with microorganisms.
There is a correlation between COD and BOD, however, it must be experimentally established before using one parameter to express another. Usually COD analysis (which is a much faster and more accurate method) is used to estimate BOD using the established correlation.
|
| 為什麼要測 COD? |
|
Why Measure Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)?
When treated wastewater is discharged into the environment, it can introduce pollution in the form of organic content to receiving waters. High levels of wastewater COD indicate concentrations of organics that can deplete dissolved oxygen in the water, leading to negative environmental and regulatory consequences. To help determine the impact and ultimately limit the amount of organic pollution in water, oxygen demand is an essential measurement.
At Hach®, find the testing equipment, resources, training and software for COD measurement and management during water treatment.
在自然界的循環中,水中的還原性物質,特別是有機化合物在生物氧化降解過程中消耗溶解氧而造成水體氧的缺損,溶解氧的缺損會破壞環境和生物群落的生態平衡,引起水質惡化,甚至發生溶氧消耗殆盡,厭氧菌滋生,造成水體變黑發臭。這就需要針對水中的有機物進行監測。
由於有機化合物有數百萬種,難以分別定性定量監測。在實踐的基礎上,環境分析學家尋求到另一種途徑,確定一種綜合指標,利用有機化合物的還原性質,將耗氧的量作為一項新的指標,這樣化學需氧量和生化需氧量就應運而生。
由於生物氧化是一個緩慢的過程,一個月的時間也只能氧化到70%左右,這對污染治理的實際操作就顯得滯後,分析化學家們將生物氧化的碳化部分定為五日生化需氧量(BOD 5),雖在某種程度上縮短了時間,但仍顯得漫長。在這種情況下,就出現了化學需氧量。
Municipal and Industrial Wastewater Treatment 民生污水和工業廢水處理
Influent waters entering wastewater plants are high in organics and the wastewater plant must reduce the “organic loading” before discharging water to a receiving body.
Knowledge of oxygen demand is useful throughout the treatment for measuring waste loading, evaluating the efficiency of the process and ensuring compliance with regulations for the oxygen demand of effluent.
Primary Treatment: 初級處理
Clarifiers, or sedimentation basins, slow the flow of the wastewater to allow suspended solids to settle. Surface skimmers collect any floating fats, oils and greases. With the use of this mechanical and physical means, approximately 30% of organic matter is removed from the wastewater and is routed to the solids management area of the plant. Secondary Treatment: 二級處理 This process uses living organisms to aid in reducing organics. In the aeration basin, bacteria and microorganisms convert biodegradable organic matter to carbon dioxide and water. With this conversion, organics are reduced, thereby reducing oxygen demand.
Discharge Limits: 排放限值
Discharge limits vary from plant to plant depending on the characteristics of the receiving water, effects on aquatic life, recreational uses and other factors. Discharge permits may stipulate a specific maximum concentration for BOD or COD, or a percent removal. Some plants require achieving as much as 90% removal of oxygen demand.  |
| 水質 COD 濃度高對環境和人體有哪些影響? |
|
COD是化學需氧量的代號,是指在強酸並加熱(使用標準COD消解器)的條件下,用重鉻酸鉀作為氧化劑處理水樣時所消化的氧化劑的量,以氧的mg/L來表示。 COD反映了水中受還原性物質污染的程度,水中的還原性物質包括有機物(為主)、亞硝酸鹽、硫化物、亞鐵鹽等。因此,化學需氧量(COD)又往往作為衡量水中有機物質含量多少的指標。 COD越高,說明水體受有機物的污染越嚴重。
當COD很高時,就會造成自然水體水質的惡化,原因在於,水體自淨需要把這些有機物給降解,COD的降解肯定需要耗氧,而水體中的複氧能力不可能滿足要求,水中DO就會直接降為0,成為厭氧狀態,在厭氧狀態也要繼續分解(微生物的厭氧處理),水體就會發黑、發臭(厭氧微生物是看起來很黑,有硫化氫氣體生成)。
說到底, 危害進入自然水體,破壞水體平衡,造成除微生物外幾乎所有生物的死亡,不僅危害水體的生物如魚類,而且還可經過食物鏈的富集,最後進入人體,引起慢性中毒。自然生活在這種環境下的人群的健康狀態就會每況愈下。 一般高COD的工業廢水中都含有很多揮發性刺激性物質,而這些稠環芳香化合物惠長期滯留在人體內,損壞某些特定的組織器官,比如說沉積在肺、腎等重要組織器官,破壞肝功能,造成生理障礙,或損害神經系統功能和引起癌症等,對於懷孕者, 這些危害物質即可能有導致畸胎之風險。
|
| 如何選擇 COD 測量儀器? |
|
COD測量相關的儀器種類十分豐富,如COD加熱反應爐、COD消解器、COD快速檢測儀、COD線上監測儀等。
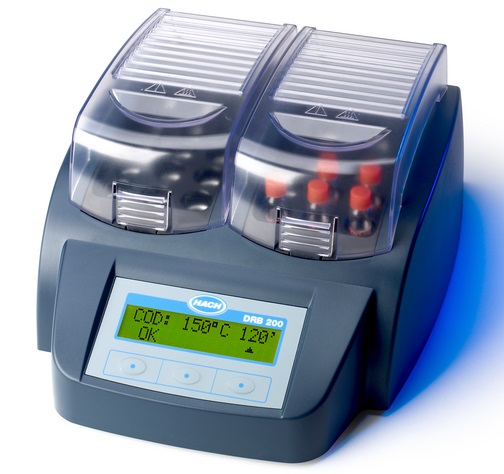
COD加熱反應爐和COD消解器是手動操作COD測量實驗時所使用的加熱回流及消解用儀器。
COD快速檢測儀可在極短時間內測量水樣的COD值,適於企業自行監督與測量活動。COD線上監測儀則是適用於連接環保單位監控網路的線上COD監測應用。
|
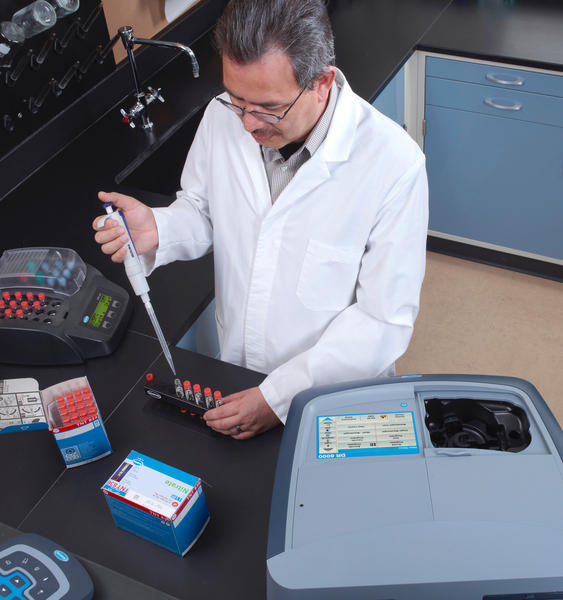
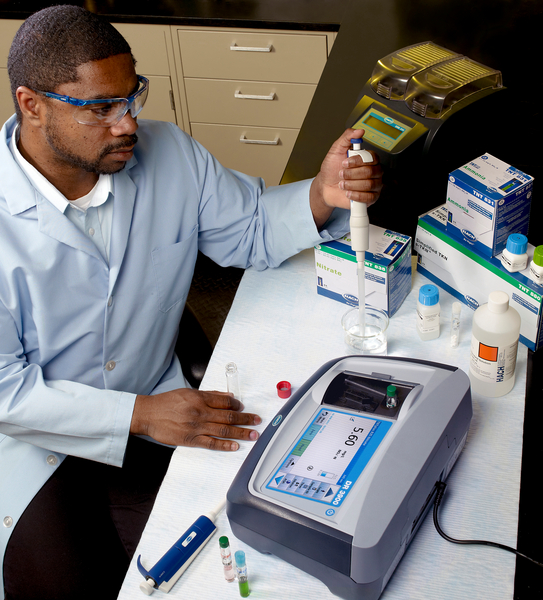
| Hach 提供COD微回流測試法的完整分析方案,方案包括Hach 分光光度計/比色計,DRB200消解器以及配套的Hach COD預製試劑等 |
|
使用Hach COD分析系統,使用者無需配製試劑,操作過程簡單、快速、經濟,測試結果與傳統滴定法具有良好的比對性,而且可將COD測試過程產生的二次污染降到最低限度。
|